The Benefits of Regular Check-Ups With a Dermatologist
December 22, 2025
Exploring the Aesthetics of Porcelain Veneers
January 3, 2026Dermatology focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of conditions affecting the skin, hair, and nails. Dermatologists manage concerns from acne to skin cancer, and innovations in this field provide many options for addressing skin health and appearance. Here are some treatments for common skin conditions:
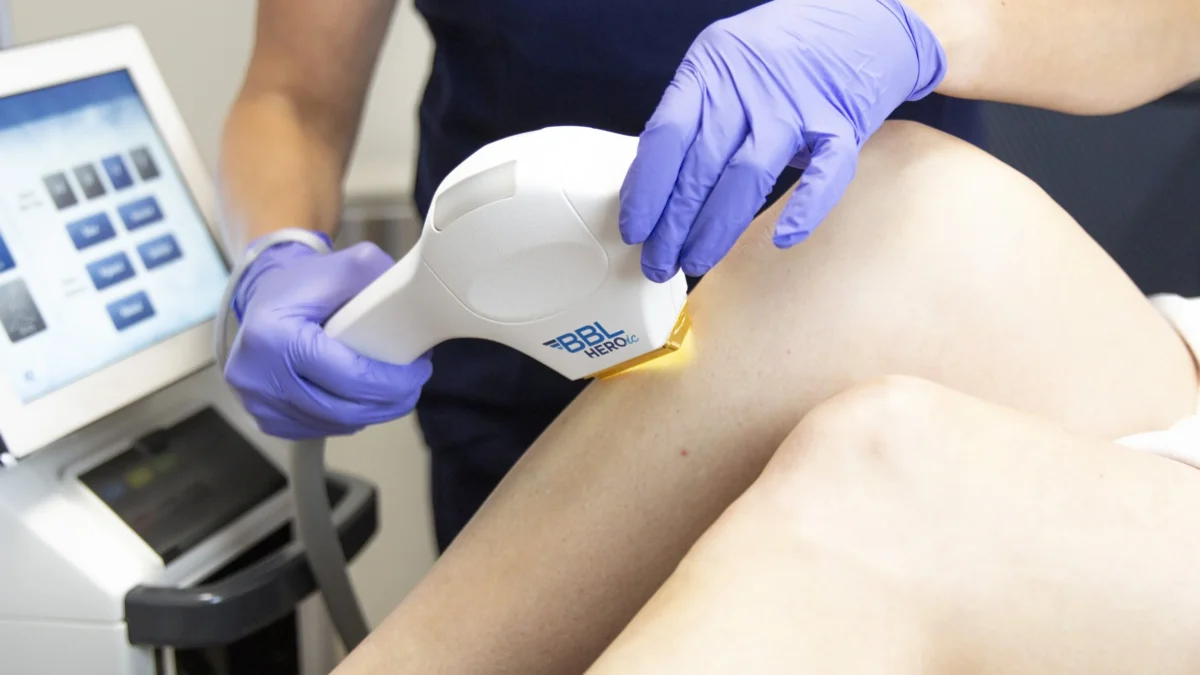
Laser and Light Therapies for Skin Growths
Lasers use focused beams of light to target skin growths without damaging surrounding areas. This precision makes them suitable for treating warts, skin tags, and seborrheic keratoses. Carbon dioxide lasers vaporize the growth layer by layer, and pulsed dye lasers target blood vessels within growths, which causes them to shrink and disappear.
Light therapies apply a photosensitizing agent to the skin before exposing it to a specific wavelength of light. This process activates the medication, which destroys the targeted cells. Recovery times vary depending on the intensity of the procedure used, and patients might experience redness or swelling at the treatment site for a few days. The choice between laser therapy and light therapy depends on the type, size, and location of the growth.
Chemical Peels for Skin Rejuvenation
Chemical peels use various solutions to exfoliate the skin’s outer layers, prompting healing and revealing a smoother, more even layer underneath. Different skin types react differently to chemical agents, so a dermatologist assesses skin characteristics to determine the appropriate depth and type of peel. Peel types include:
- Superficial peels: These use mild acids, such as alpha-hydroxy acids, to exfoliate. They are often used for minor discoloration or rough texture.
- Medium peels: These penetrate more deeply to address moderate wrinkles, acne scars, and uneven skin tone; trichloroacetic acid is a common agent for medium-depth treatments.
- Deep peels: These reach the lower dermal layer for significant skin resurfacing, and phenol is typically used for these stronger treatments. The recovery process involves peeling and redness that may last a few days or several weeks.
Medications for Chronic Conditions
Managing chronic skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, and acne often requires a multifaceted approach that includes medication. Biologics are a type of medication, and they target the part of the immune system that drives inflammation. They are typically administered via injection or intravenous infusion.
Topical treatments are a primary option for many dermatology patients. Retinoids help unclog pores and reduce inflammation associated with acne, and corticosteroids reduce swelling and redness in various dermatitis conditions. Non-steroidal topical creams offer options for long-term management with fewer side effects. Systemic medications, taken orally, address widespread or resistant cases.
Each medication carries a unique profile of potential side effects and interactions. A dermatologist will track treatment progress, and they manage any adverse reactions. Adherence to the prescribed regimen influences the effectiveness of these pharmaceutical interventions.
Visit a Dermatology Clinic
Consulting a dermatologist provides a pathway to understanding specific skin needs and treatment options. These specialists evaluate individual conditions to recommend appropriate therapies based on medical history and skin type, and regular check-ups monitor skin health and detect potential issues early. Schedule a dermatology appointment today to discuss your skin concerns.