Meal Plans for Weight Management: A Complete Guide to Eating Smart
November 14, 2025
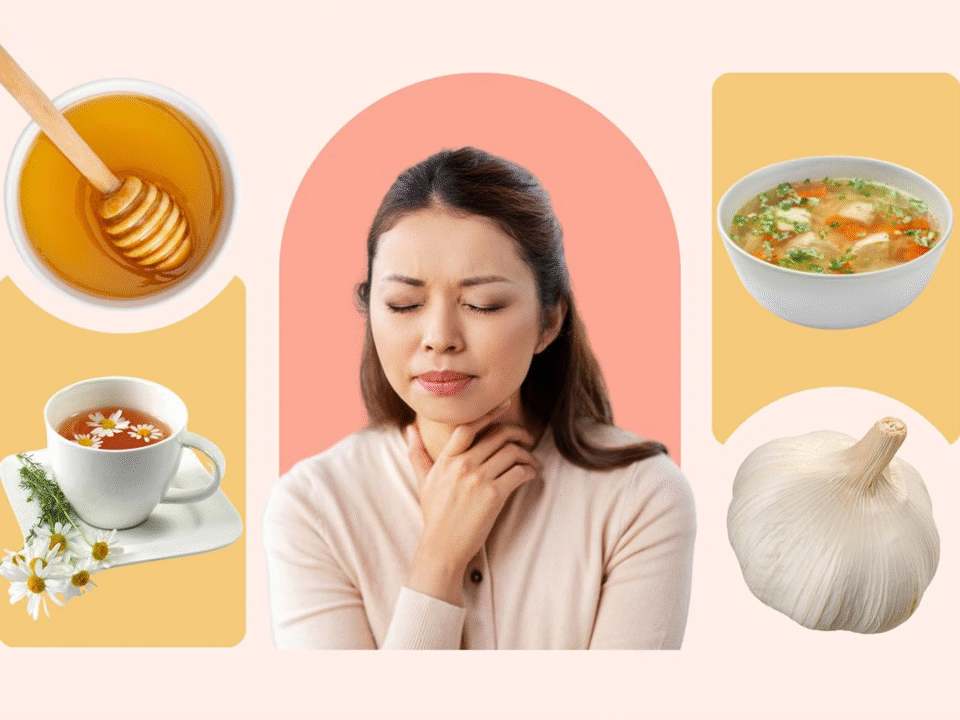
Home Remedies for Sore Throat: Natural Ways to Soothe Your Pain
November 14, 2025Sinusitis, commonly known as a sinus infection, is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the sinuses—hollow spaces in the bones around the nose—become inflamed and swollen. This inflammation can interfere with the normal drainage of mucus, leading to discomfort and a variety of symptoms. While sinusitis is often temporary, chronic sinus infections can be more challenging and may require medical attention. Understanding the symptoms and treatments is essential for effective management.
Understanding Sinusitis
Sinusitis can be classified into two main types: acute and chronic.
- Acute sinusitis usually lasts for a short period, often less than four weeks, and is commonly caused by viral infections, such as the common cold.
- Chronic sinusitis lasts for more than 12 weeks and can be caused by infections, nasal polyps, or structural issues in the sinuses.
The sinuses include the frontal sinuses (forehead area), maxillary sinuses (cheek area), ethmoid sinuses (between the eyes), and sphenoid sinuses (behind the eyes). When these areas swell or get blocked, mucus cannot drain properly, leading to infection and pressure.
Common Symptoms of Sinusitis
Recognizing the symptoms of sinusitis is the first step toward treatment. While symptoms can vary from person to person, some of the most common signs include:
- Nasal Congestion
One of the hallmark signs of sinusitis is nasal congestion. People often feel that their nose is blocked or stuffy, making it hard to breathe through the nose. - Facial Pain or Pressure
Swelling in the sinuses can cause pain or pressure around the forehead, cheeks, eyes, or the bridge of the nose. This discomfort often worsens when bending forward or lying down. - Thick Nasal Discharge
Sinus infections frequently cause thick, yellow or green nasal discharge. In some cases, discharge can also drain down the back of the throat, causing a sore throat or cough. - Headaches
Pressure in the sinuses can trigger headaches, often located in the forehead or around the eyes. These headaches may worsen in the morning or when the weather changes. - Fever
Although more common in acute sinusitis, fever can indicate a bacterial infection that may need medical treatment. - Reduced Sense of Smell or Taste
Swelling in the nasal passages can reduce the sense of smell, which can also affect the ability to taste food properly. - Fatigue
Chronic sinus infections can make a person feel tired and sluggish due to persistent discomfort and disrupted sleep.
Causes and Risk Factors
Sinusitis can result from various causes, including:
- Viral Infections: The most common cause, often following a cold or flu.
- Bacterial Infections: Occur when a viral infection worsens or doesn’t resolve, leading to a bacterial sinus infection.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can trigger inflammation and swelling in the sinuses.
- Nasal Polyps: Small growths in the nasal passages can block sinus drainage.
- Deviated Septum: A structural issue in the nose can interfere with mucus drainage.
- Immune System Disorders: Conditions that weaken the immune system can increase susceptibility.
Certain risk factors, like smoking, frequent air travel, or exposure to pollutants, can also increase the likelihood of developing sinusitis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for sinusitis depends on the type and severity of the infection. Here are the main approaches:
1. Home Remedies and Self-Care
For mild cases of acute sinusitis, self-care measures can be highly effective:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps thin mucus, making it easier to drain.
- Steam Inhalation: Breathing in steam from a bowl of hot water or a warm shower can relieve nasal congestion.
- Saline Nasal Sprays: These sprays help rinse the nasal passages, reduce inflammation, and flush out mucus.
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm cloth over the face can ease facial pain and pressure.
- Rest: Adequate rest supports the immune system in fighting the infection.
2. Medications
When home remedies aren’t enough, medications may be needed:
- Decongestants: These reduce nasal swelling and improve sinus drainage. They are available as pills or nasal sprays but should not be used for more than a few days.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help manage headaches and facial pain.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed only for bacterial sinus infections. Viral infections do not respond to antibiotics.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: These sprays reduce inflammation in the nasal passages and are useful for chronic or allergy-related sinusitis.
3. Surgery
In severe or chronic cases that do not respond to medication, surgical intervention may be necessary:
- Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS): A minimally invasive procedure to remove blockages and improve sinus drainage.
- Balloon Sinuplasty: A newer technique that widens sinus passages using a small balloon.
Preventive Measures
Preventing sinusitis is often easier than treating it. Some tips include:
- Wash hands frequently to prevent viral infections.
- Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Manage allergies with proper medications and avoidance strategies.
- Use a humidifier in dry environments to keep nasal passages moist.
- Practice good nasal hygiene, including saline sprays if prone to sinus infections.
When to See a Doctor
Most cases of acute sinusitis resolve within 7–10 days. However, you should see a doctor if:
- Symptoms persist beyond 10 days.
- Fever is high or persistent.
- There is severe facial pain or swelling.
- Vision changes or severe headache occurs.
- You experience repeated sinus infections over a short period.
Chronic sinusitis may require long-term treatment and sometimes imaging tests to identify underlying causes.
5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can sinusitis go away on its own?
Yes, most acute sinus infections caused by viruses improve on their own within 7–10 days. Home remedies and rest often help speed up recovery.
2. How long does chronic sinusitis last?
Chronic sinusitis lasts more than 12 weeks and may require medical intervention, including medications or surgery, depending on the underlying cause.
3. Is sinusitis contagious?
Viral sinusitis can be contagious because it often starts with a cold. Bacterial sinusitis, however, is generally not contagious.
4. Can allergies cause sinusitis?
Yes, allergies can trigger inflammation in the sinuses, leading to blockage and infection. Managing allergies can help prevent sinusitis.
5. Are antibiotics always needed for sinus infections?
No, antibiotics are only effective for bacterial sinus infections. Most viral sinus infections do not require antibiotics and improve with self-care.
Conclusion
Sinusitis is a common but often manageable condition. Recognizing the symptoms early and taking appropriate measures—ranging from home remedies to medical treatments—can help relieve discomfort and prevent complications. By maintaining good nasal hygiene, managing allergies, and seeking timely medical advice when necessary, most people can recover fully and reduce the risk of chronic sinus issues. Understanding your sinuses and how they function is key to keeping them healthy and avoiding repeated infections